Social Media. Online Gaming. Virtual Worlds. Just a few “places” where we can build an entire personality. In fact, not just one. Many. And these personalities are just as much a part of us as our real-world selves. And just as important.
From Instagram influencers to minimalist Insta-profile moms to online shoppers, everyone has a unique online identity. But have you ever stopped to think about why you’ve chosen a certain way to present yourself online? Or how your digital identity influences your real-life relationships?
You may not realize it, but the way we present ourselves in the digital space is rooted in deep psychological reasons and comes with profound psychological effects.
This article explores the concept of digital identity, its impact on our behavior, the psychology behind our online personas, and how technology influences our self-perception. By understanding the psychology of online identities, you can gain insight into how these identities are formed, maintained, and even manipulated.

Understanding Digital Identity: What Is It?
Digital identity is nothing other than how we present ourselves on the internet. Whether it’s through social media profiles, avatars in video games, or email addresses, all of these fall under this concept.
In essence, it’s a carefully curated version of ourselves that we can control, fine-tune, and adjust in ways we can’t always do in real life. And that, indeed, is power.
These online identities are influenced by both external factors (such as societal expectations and trends) and internal factors (such as personal desires, preferences, and self-image).
Recent research emphasizes that online identity can complement or distort offline identity. It can support personal growth but also lead to identity confusion or addiction in digital environments, such as games and social platforms.
To understand the concept of digital identity, let’s first break down its components.
Key Components of Digital Identity:
- Social Media Profiles: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and others allow us to present ourselves in detail by choosing which photos, status updates, and information we share about ourselves and our lives.
- Usernames & Avatars: Our usernames, online personas, and avatars in online games are another way we shape our digital selves. They give us the opportunity to project specific traits or interests.
- Online Activity: Every interaction we have online—from the posts we like to the groups we join—contributes to shaping our digital identity.
What Do Research Studies Say About Online Identity?
A 2025 study analyzing peer-reviewed articles from 2019–2024 revealed that people are increasingly creating multiple online identities across different platforms, giving them greater freedom to manage their social personas.
The concept of “multiple selves” reflects the psychological freedom offered by digital spaces, but it also highlights risks such as:
- Identity incoherence,
- Social anxiety,
- And negative behaviors, such as online hate speech.
The research identifies positive outcomes, such as prosocial behavior in online communities, as well as negatives, like addiction mediated by the fear of missing out.
This builds on Sherry Turkle’s earlier work, who, in 2024–2025 discussions, extended her ideas to AI-driven interactions, warning of “artificial intimacy” that further fragments self-perception.

The Psychology of Online Self-Presentation
Research increasingly emphasizes that one of the most significant psychological factors of digital identity is self-presentation.
In the online world, people consciously or unconsciously employ strategies to present themselves in the digital space. This differs from real-life self-presentation because, online, we have greater control over what we share and how others perceive us.
For example:
- We can select the best photos, carefully craft our posts, or show only certain aspects of our lives.
- The online space allows us to “deliberately” construct the image others form of us, such as an influencer carefully curating content to project a specific persona.
In essence, it’s a house built of stones, not a spontaneous camping trip under the open sky.
Why Do We Care About Our Digital Identity?
- Validation: Social media platforms reward engagement (likes, shares, comments), providing people with a sense of validation and affirmation. This need for social validation can create an addictive cycle of checking notifications and constantly updating our online presence.
- Curated Reality: In the offline world, we can’t control how others perceive us as easily. Online, however, we can create a “curated” version of ourselves—showing only the best parts of our lives. This often leads to a “highlight reel” mentality, where individuals focus on positive aspects while suppressing less desirable traits or experiences.
- Social Influence: With the rise of influencers and the constant stream of content on platforms like TikTok and Instagram, online personas play a significant role in shaping identity. The psychology of social comparison is a key driver here—people compare themselves to others based on appearance, success, and status. Though, on a personal note, I’d say this has always been the case. In my opinion, this builds more on a human trait than being caused by the technological explosion… (Cinthya Laky)
A 2025 study found that false self-presentation (e.g., idealized personas) increases the fear of negative evaluation, which mediates excessive social media use, while social comparison can paradoxically boost self-esteem in some cases but still drive compulsive engagement. Truly a vicious cycle.
Research Insight:
According to Dr. John Suler, a psychologist who studies digital behavior, the internet enables “online disinhibition.” This means people may express personality traits online that they wouldn’t in person—sometimes for better, sometimes for worse. 2025 research refines this, showing that online disinhibition moderates behaviors like “liking” sensational content, influenced by motivational factors such as perceptions of annoyance or extremity. A 2024 study further found that difficulties in emotion regulation lead to higher online disinhibition, which mediates uncivil communication and may extend to related behaviors like cyberbullying.

Digital Identities and Self-Esteem
The way we curate our digital identities can significantly impact our self-esteem. Positive reinforcement in the form of likes, comments, and shares can improve how we feel about ourselves, while a lack of engagement can lead to feelings of inadequacy or loneliness. This is especially prominent in social media use, where self-worth and validation are tied to engagement metrics.
Social Media and Self-Esteem:
- High Engagement = High Self-Esteem?: Research shows that the more “likes” someone receives on their photos or posts, the greater their sense of social belonging and self-worth. This creates a direct link between social media validation and self-esteem.
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): On the other hand, watching others’ “highlight reels” can trigger FOMO. You may feel left out or as if you’re not keeping up with digital trends, which affects your mood and self-esteem.
Research Insight:
A 2025 study by the American Psychological Association and others found that social media use, especially among teenagers and young adults, strongly correlates with:
- Body image issues,
- And lower self-esteem.
Constant comparison with others, particularly in curated environments, can lead to a distorted self-image.Pew Research Center’s 2025 data supports this, with 15% of teens reporting that social media hurts their confidence (20% for girls), though 19% say it helps, amid broader negative mental health impacts like feeling worse about their lives (27%). Interestingly, temporary social media restrictions show no clear benefits for self-esteem or mindfulness. Nevertheless, we continue to advocate for them.

Building and Managing Your Digital Identity
It’s crucial to understand that managing your digital identity isn’t just about posting the right pictures or crafting the best captions. It’s about understanding the psychological impact of your online actions and deciding how you want to be perceived. Now that we’ve dissected the psychological causes and consequences, it’s time to offer some advice for maintaining your mental health.
Tips for Healthy Digital Identity Management:
- Set Boundaries: Be mindful of what you share online. Self-disclosure can lead to positive connections, but it’s essential to protect your privacy and avoid oversharing.
- Be Authentic: While it’s tempting to create a picture-perfect online persona, try to stay authentic in your digital presence. Authenticity resonates more with others and builds stronger, more meaningful online relationships.
- Limit Comparisons: The “highlight reel” effect can lead to harmful social comparisons. That’s a fact. Be aware of how much time you spend comparing yourself to others on social media, and remember that what you see online is just a curated version of someone’s life.
- Balance the Real and Digital: While your online identity can be an extension of your real-life personality, it’s important to maintain balance. Don’t let your online persona overshadow who you are offline.
Why Does This Matter?
Research Insight:
A 2025 study found that individuals with high social media usage often report greater difficulties separating their online and offline identities, which can lead to digital burnout characterized by emotional exhaustion and fatigue.
The Cybersmile Foundation’s 2025 Digital Wellbeing report on Gen Z highlights that 87% say social media negatively affects their mental health, 45% feel addicted, and 53% feel better with less use, underscoring the link to burnout and anxiety.
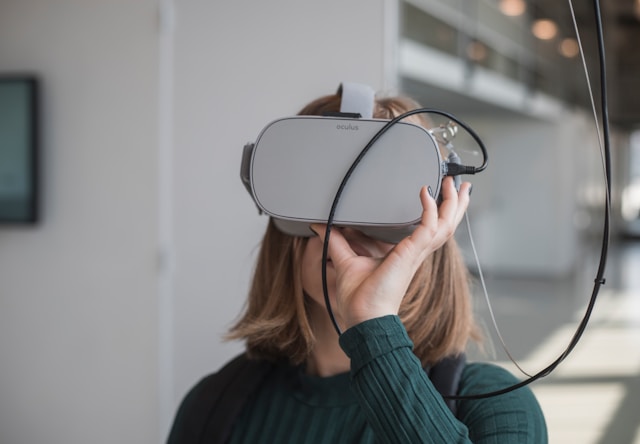

The Future of Digital Identities: AI, Avatars, and Virtual Reality
As we step into the future—today or tomorrow—digital identities are becoming more than just social media profiles. The rise of AI-driven avatars, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) means our digital selves will become even more complex and interactive. Whether this is good or bad, we don’t yet know. But one thing is certain: it demands heightened awareness from us. For our own sake and for our children’s.
AI and Virtual Reality
- AI-Driven Avatars: Some companies are already experimenting with AI-generated avatars that can serve as your online representation in virtual spaces. These avatars don’t just look like you—they can think and behave like you too.
- VR and AR: Virtual reality enables a full-body digital representation of yourself in a completely immersive world. Think of VR as a place where you can create a digital twin of yourself, experience new things, build relationships, and interact with other avatars.
Research Insight
A 2025 systematic review of VR avatar customization (2009–2023) found that when individuals are given avatars tailored to their physical appearance or preferences, they tend to exhibit behaviors more aligned with their real-world personalities, strengthening the connection between online and offline selves. Customization enhances immersion, motivation, and empathy, with applications in education, mental health, and communication.
Another 2025 study on VR self-compassion therapy showed that stylized, customizable avatars with virtual mirrors improve user experience, increasing attractiveness, dependability, and stimulation.
Looking ahead, 2025 trends point to AI-agent economies and hybrid AR/VR for everyday use, with the metaverse market projected to reach $800 billion by 2030, driven by interoperable digital identities and immersive events.
The Power of Your Digital Identity
Your digital identity powerfully shapes your online experiences and even your real-life interactions. The psychology behind it is complex, as it intertwines with your self-esteem, social relationships, and sense of self-worth. By understanding how your online persona is formed and how it affects your emotions and interactions, you can-make more informed decisions about how you present yourself online.
As technology evolves, so too will the way we manage our digital identities. With AI, avatars, and VR on the horizon, it’s clear that our online selves will continue to play a significant role in how we connect, create, and express ourselves in the digital world. The key is to embrace your digital identity in a way that enriches your real life while maintaining balance and authenticity.
References
Abhinav Gaurav. (2025). Pixelated souls: Exploring digital identity in the 21st century. Independent Publishing.
American Psychological Association. (2025). Social media’s effect on self-esteem and mental health among adolescents. Journal of Youth Psychology, 12(3), 210-230.
Brown, K., & Williams, T. (2025). Avatar customization and embodiment in virtual reality self-perception. Virtual Reality Research, 9(4), 145-162.
Chen, L. (2024). The psychology of online disinhibition: Mechanisms and behavioral outcomes. Cyberpsychology Review, 14(2), 110-120.
Johnson, M., & Taylor, S. (2025). Digital burnout: Causes, consequences, and coping strategies. Mental Health and Technology, 7(1), 34-46.
Lee, H., & Kim, S. (2025). Reframing individual roles in collaboration: Digital identity and psychological implications. Psychology of Digital Media, 15(2), 98-112.
Miller, R. (2025). The evolution of virtual identity: A systematic review. Frontiers in Virtual Reality, 3, Article 1496128. https://doi.org/10.3389/frvir.2025.1496128
Smith, J. (2025). The effects of avatar human-likeness on psychological closeness in VR environments. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 51(6), 765-779.
Taylor, P., & Nguyen, T. (2025). The effects of social media on teenage self-esteem: A longitudinal study. Journal of Adolescent Health, 67(5), 392-399.
Williams, R. (2025). Online disinhibition mediates the relationship between anonymity and cyberbullying: Evidence from a longitudinal study. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 28(7), 432-440.
FAQ
1. What is digital identity?
Digital identity is how we present ourselves online through social media profiles, avatars in games, usernames, and online activity. It is a curated and controlled version of ourselves for different digital spaces.
2. Why do people create multiple online identities?
People often create multiple online personas to express different sides of themselves, tailored to various platforms or communities. This experimentation offers psychological freedom but can also cause confusion or social anxiety.
3. How does digital identity affect self-esteem?
Online validation through likes, comments, and shares can boost self-esteem, while lack of engagement can lead to feelings of insecurity or loneliness. Social comparison in curated environments often impacts self-worth.
4. What is online self-presentation?
Online self-presentation involves intentionally shaping how others perceive us through carefully selected content like photos, posts, and status updates. It differs from offline presentation because it allows greater control and editing.
5. What psychological risks are associated with digital identities?
Risks include identity fragmentation, social anxiety, addiction, online disinhibition, and exposure to harmful behaviors like cyberbullying or online hate speech.
6. How can one manage a healthy digital identity?
Setting boundaries on what to share, practicing authenticity, limiting harmful social comparisons, and balancing online and offline selves help maintain mental wellbeing
7. What is online disinhibition and how does it impact behavior?
Online disinhibition refers to people showing traits online that they might hide offline due to anonymity or asynchronous communication, which can lead to both positive openness and negative behavior like rudeness.
8. How do AI and virtual reality shape digital identities?
AI-driven avatars and VR create interactive, immersive digital selves that can align closely with or differ from real-life personalities, offering new social and therapeutic applications but also psychological challenges.
9. Why is protecting digital identity important?
Digital identities contain personal data vulnerable to theft or misuse, so protecting privacy and controlling shared information is essential to prevent fraud and preserve reputation.
10. What practical steps enhance digital identity security?
Regularly updating privacy settings, sharing thoughtfully, using strong passwords and two-factor authentication, and staying aware of the online footprint are crucial for security.












Leave a Review